ScalarDB Overview
This page describes what ScalarDB is and its primary use cases.
What is ScalarDB?
ScalarDB is a hybrid transaction/analytical processing (HTAP) engine for diverse databases. It runs as middleware on databases and virtually unifies diverse databases by achieving ACID transactions and real-time analytics across them to simplify the complexity of managing multiple databases or multiple instances of a single database.
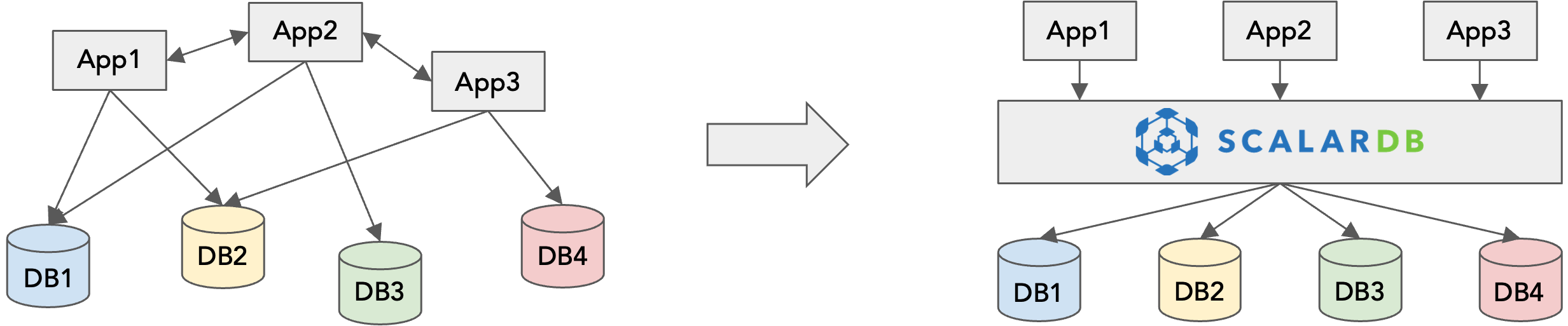
As a versatile solution, ScalarDB supports a range of databases, including:
- Relational databases that support JDBC, such as MariaDB, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle Database, PostgreSQL, SQLite, and their compatible databases, like Amazon Aurora, Google AlloyDB, TiDB, and YugabyteDB.
- NoSQL databases like Amazon DynamoDB, Apache Cassandra, and Azure Cosmos DB.
For details on which databases ScalarDB supports, refer to Supported Databases.
Why ScalarDB?
Several solutions, such as global transaction managers, data federation engines, and HTAP systems, have similar goals, but they are limited in the following perspectives:
- Global transaction managers (like Oracle MicroTx and Atomikos) are designed to run transactions across a limited set of heterogeneous databases (like only XA-compliant databases).
- Data federation engines (like Denodo and Starburst) are designed to run analytical queries across heterogeneous databases.
- HTAP systems (like TiDB and SingleStore) run both transactions and analytical queries only on homogeneous databases.
In other words, they virtually unify databases, but with limitations. For example, with data federation engines, users can run read-only analytical queries on a virtualized view across multiple databases. However, they often need to run update queries separately for each database.
Unlike other solutions, ScalarDB stands out by offering the ability to run both transactional and analytical queries on heterogeneous databases, which can significantly simplify database management.
The following table summarizes how ScalarDB is different from the other solutions.
| Transactions across heterogeneous databases | Analytics across heterogeneous databases | |
|---|---|---|
| Global transaction managers (like Oracle MicroTx and Atomikos) | Yes (but existing solutions support only a limited set of databases) | No |
| Data federation engines (like Denodo and Starburst) | No | Yes |
| HTAP systems (like TiDB and SingleStore) | No (support homogeneous databases only) | No (support homogeneous databases only) |
| ScalarDB | Yes (supports various databases) | Yes |
ScalarDB use cases
ScalarDB can be used in various ways. Here are the three primary use cases of ScalarDB.
Managing siloed databases easily
Many enterprises comprise several organizations, departments, and business units to support agile business operations, which often leads to siloed information systems. In particular, different organizations likely manage different applications with different databases. Managing such siloed databases is challenging because applications must communicate with each database separately and properly deal with the differences between databases.
ScalarDB simplifies the management of siloed databases with a unified interface, enabling users to treat the databases as if they were a single database. For example, users can run (analytical) join queries over multiple databases without interacting with the databases respectively.
Managing consistency between multiple database
Modern architectures, like the microservice architecture, encourage a system to separate a service and its database into smaller subsets to increase system modularity and development efficiency. However, managing diverse databases, especially of different kinds, is challenging because applications must ensure the correct states (or, in other words, consistencies) of those databases, even using transaction management patterns like Saga and TCC.
ScalarDB simplifies managing such diverse databases with a correctness guarantee (or, in other words, ACID with strict serializability), enabling you to focus on application development without worrying about guaranteeing consistency between databases.
Reducing database migration hurdles
Applications tend to be locked into using a certain database because of the specific capabilities that the database provides. Such database lock-in discourages upgrading or changing the database because doing so often requires rewriting the application.
ScalarDB provides a unified interface for diverse databases. Thus, once an application is written by using the ScalarDB interface, it becomes portable, which helps to achieve seamless database migration without rewriting the application.