Getting Started with ScalarDB
This getting started tutorial explains how to configure your preferred database in ScalarDB and illustrates the process of creating a sample e-commerce application, where items can be ordered and paid for with a credit card by using ScalarDB. The sample e-commerce application shows how users can order and pay for items by using a line of credit.
Since the focus of the sample application is to demonstrate using ScalarDB, application-specific error handling, authentication processing, and similar functions are not included in the sample application. For details about exception handling in ScalarDB, see How to handle exceptions.
Prerequisites for this sample application
- OpenJDK LTS version (8, 11, 17, or 21) from Eclipse Temurin
- Docker 20.10 or later with Docker Compose V2 or later
This sample application has been tested with OpenJDK from Eclipse Temurin. ScalarDB itself, however, has been tested with JDK distributions from various vendors. For details about the requirements for ScalarDB, including compatible JDK distributions, please see Requirements.
Clone the ScalarDB samples repository
Open Terminal, then clone the ScalarDB samples repository by running the following command:
git clone https://github.com/scalar-labs/scalardb-samples
Then, go to the directory that contains the sample application by running the following command:
cd scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample
Set up your database for ScalarDB
Select your database, and follow the instructions to configure it for ScalarDB.
For a list of databases that ScalarDB supports, see Databases.
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- Oracle Database
- SQL Server
- DynamoDB
- Cosmos DB for NoSQL
- Cassandra
Run MySQL locally
You can run MySQL in Docker Compose by using the docker-compose.yml file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory.
To start MySQL, run the following command:
docker compose up -d mysql
Configure ScalarDB
The database.properties file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory contains database configurations for ScalarDB. Please uncomment the properties for MySQL in the database.properties file so that the configuration looks as follows:
# For MySQL
scalar.db.storage=jdbc
scalar.db.contact_points=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/
scalar.db.username=root
scalar.db.password=mysql
Run PostgreSQL locally
You can run PostgreSQL in Docker Compose by using the docker-compose.yml file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory.
To start PostgreSQL, run the following command:
docker compose up -d postgres
Configure ScalarDB
The database.properties file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory contains database configurations for ScalarDB. Please uncomment the properties for PostgreSQL in the database.properties file so that the configuration looks as follows:
# For PostgreSQL
scalar.db.storage=jdbc
scalar.db.contact_points=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/
scalar.db.username=postgres
scalar.db.password=postgres
Run Oracle Database locally
You can run Oracle Database in Docker Compose by using the docker-compose.yml file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory.
To start Oracle Database, run the following command:
docker compose up -d oracle
Configure ScalarDB
The database.properties file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory contains database configurations for ScalarDB. Please uncomment the properties for Oracle Database in the database.properties file so that the configuration looks as follows:
# For Oracle
scalar.db.storage=jdbc
scalar.db.contact_points=jdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:1521/FREEPDB1
scalar.db.username=SYSTEM
scalar.db.password=Oracle
Run SQL Server locally
You can run SQL Server in Docker Compose by using the docker-compose.yml file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory.
To start SQL Server, run the following command:
docker compose up -d sqlserver
Configure ScalarDB
The database.properties file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory contains database configurations for ScalarDB. Please uncomment the properties for SQL Server in the database.properties file so that the configuration looks as follows:
# For SQL Server
scalar.db.storage=jdbc
scalar.db.contact_points=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=true
scalar.db.username=sa
scalar.db.password=SqlServer22
Run Amazon DynamoDB Local
You can run Amazon DynamoDB Local in Docker Compose by using the docker-compose.yml file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory.
To start Amazon DynamoDB Local, run the following command:
docker compose up -d dynamodb
Configure ScalarDB
The database.properties file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory contains database configurations for ScalarDB. Please uncomment the properties for Amazon DynamoDB Local in the database.properties file so that the configuration looks as follows:
# For DynamoDB Local
scalar.db.storage=dynamo
scalar.db.contact_points=sample
scalar.db.username=sample
scalar.db.password=sample
scalar.db.dynamo.endpoint_override=http://localhost:8000
To use Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL, you must have an Azure account. If you don't have an Azure account, visit Create an Azure Cosmos DB account.
Configure Cosmos DB for NoSQL
Set the default consistency level to Strong according to the official document at Configure the default consistency level.
Configure ScalarDB
The following instructions assume that you have properly installed and configured the JDK in your local environment and properly configured your Cosmos DB for NoSQL account in Azure.
The database.properties file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory contains database configurations for ScalarDB. Be sure to change the values for scalar.db.contact_points and scalar.db.password as described.
# For Cosmos DB
scalar.db.storage=cosmos
scalar.db.contact_points=<COSMOS_DB_FOR_NOSQL_URI>
scalar.db.password=<COSMOS_DB_FOR_NOSQL_KEY>
You can use the primary key or the secondary key in your Azure Cosmos DB account as the value for scalar.db.password.
Run Cassandra locally
You can run Apache Cassandra in Docker Compose by using the docker-compose.yml file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory.
To start Apache Cassandra, run the following command:
docker compose up -d cassandra
Configure ScalarDB
The database.properties file in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory contains database configurations for ScalarDB. Please uncomment the properties for Cassandra in the database.properties file so that the configuration looks as follows:
# For Cassandra
scalar.db.storage=cassandra
scalar.db.contact_points=localhost
scalar.db.username=cassandra
scalar.db.password=cassandra
Load the database schema
You need to define the database schema (the method in which the data will be organized) in the application. For details about the supported data types, see Data type mapping between ScalarDB and other databases.
For this tutorial, a file named schema.json already exists in the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory. To apply the schema, go to the scalardb Releases page and download the ScalarDB Schema Loader that matches the version of ScalarDB that you are using to the scalardb-samples/scalardb-sample directory.
Then, run the following command, replacing <VERSION> with the version of the ScalarDB Schema Loader that you downloaded:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- Oracle Database
- SQL Server
- DynamoDB
- Cosmos DB for NoSQL
- Cassandra
java -jar scalardb-schema-loader-<VERSION>.jar --config database.properties --schema-file schema.json --coordinator
The --coordinator option is specified because a table with transaction set to true exists in the schema. For details about configuring and loading a schema, see ScalarDB Schema Loader.
java -jar scalardb-schema-loader-<VERSION>.jar --config database.properties --schema-file schema.json --coordinator
The --coordinator option is specified because a table with transaction set to true exists in the schema. For details about configuring and loading a schema, see ScalarDB Schema Loader.
java -jar scalardb-schema-loader-<VERSION>.jar --config database.properties --schema-file schema.json --coordinator
The --coordinator option is specified because a table with transaction set to true exists in the schema. For details about configuring and loading a schema, see ScalarDB Schema Loader.
java -jar scalardb-schema-loader-<VERSION>.jar --config database.properties --schema-file schema.json --coordinator
The --coordinator option is specified because a table with transaction set to true exists in the schema. For details about configuring and loading a schema, see ScalarDB Schema Loader.
java -jar scalardb-schema-loader-<VERSION>.jar --config database.properties --schema-file schema.json --coordinator --no-backup --no-scaling
The --coordinator option is specified because a table with transaction set to true exists in the schema. For details about configuring and loading a schema, see ScalarDB Schema Loader.
Also, --no-backup and --no-scaling options are specified because Amazon DynamoDB Local does not support continuous backup and auto-scaling.
java -jar scalardb-schema-loader-<VERSION>.jar --config database.properties --schema-file schema.json --coordinator
The --coordinator option is specified because a table with transaction set to true exists in the schema. For details about configuring and loading a schema, see ScalarDB Schema Loader.
java -jar scalardb-schema-loader-<VERSION>.jar --config database.properties --schema-file schema.json --coordinator --replication-factor=1
The --coordinator option is specified because a table with transaction set to true exists in the schema. For details about configuring and loading a schema, see ScalarDB Schema Loader.
In addition, the --replication-factor=1 option has an effect only when using Cassandra. The default replication factor is 3, but to facilitate the setup in this tutorial, 1 is used so that you only need to prepare a cluster with one node instead of three nodes. However, keep in mind that a replication factor of 1 is not suited for production.
Schema details
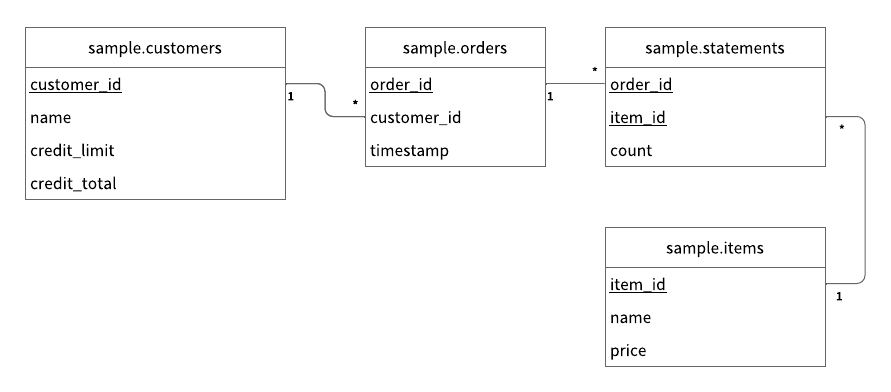
As shown in schema.json for the sample application, all the tables are created in the sample namespace.
sample.customers: a table that manages customer informationcredit_limit: the maximum amount of money that the lender will allow the customer to spend from their line of creditcredit_total: the amount of money that the customer has spent from their line of credit
sample.orders: a table that manages order informationsample.statements: a table that manages order statement informationsample.items: a table that manages information for items to be ordered
The Entity Relationship Diagram for the schema is as follows:
Load the initial data
Before running the sample application, you need to load the initial data by running the following command:
./gradlew run --args="LoadInitialData"
After the initial data has loaded, the following records should be stored in the tables.
sample.customers table
| customer_id | name | credit_limit | credit_total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yamada Taro | 10000 | 0 |
| 2 | Yamada Hanako | 10000 | 0 |
| 3 | Suzuki Ichiro | 10000 | 0 |
sample.items table
| item_id | name | price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apple | 1000 |
| 2 | Orange | 2000 |
| 3 | Grape | 2500 |
| 4 | Mango | 5000 |
| 5 | Melon | 3000 |
Execute transactions and retrieve data in the sample application
The following sections describe how to execute transactions and retrieve data in the sample e-commerce application.
Get customer information
Start with getting information about the customer whose ID is 1 by running the following command:
./gradlew run --args="GetCustomerInfo 1"
You should see the following output:
...
{"id": 1, "name": "Yamada Taro", "credit_limit": 10000, "credit_total": 0}
...
Place an order
Then, have customer ID 1 place an order for three apples and two oranges by running the following command:
The order format in this command is ./gradlew run --args="PlaceOrder <CUSTOMER_ID> <ITEM_ID>:<COUNT>,<ITEM_ID>:<COUNT>,...".
./gradlew run --args="PlaceOrder 1 1:3,2:2"
You should see a similar output as below, with a different UUID for order_id, which confirms that the order was successful:
...
{"order_id": "dea4964a-ff50-4ecf-9201-027981a1566e"}
...
Check order details
Check details about the order by running the following command, replacing <ORDER_ID_UUID> with the UUID for the order_id that was shown after running the previous command:
./gradlew run --args="GetOrder <ORDER_ID_UUID>"
You should see a similar output as below, with different UUIDs for order_id and timestamp:
...
{"order": {"order_id": "dea4964a-ff50-4ecf-9201-027981a1566e","timestamp": 1650948340914,"customer_id": 1,"customer_name": "Yamada Taro","statement": [{"item_id": 1,"item_name": "Apple","price": 1000,"count": 3,"total": 3000},{"item_id": 2,"item_name": "Orange","price": 2000,"count": 2,"total": 4000}],"total": 7000}}
...
Place another order
Place an order for one melon that uses the remaining amount in credit_total for customer ID 1 by running the following command:
./gradlew run --args="PlaceOrder 1 5:1"
You should see a similar output as below, with a different UUID for order_id, which confirms that the order was successful:
...
{"order_id": "bcc34150-91fa-4bea-83db-d2dbe6f0f30d"}
...
Check order history
Get the history of all orders for customer ID 1 by running the following command:
./gradlew run --args="GetOrders 1"
You should see a similar output as below, with different UUIDs for order_id and timestamp, which shows the history of all orders for customer ID 1 in descending order by timestamp:
...
{"order": [{"order_id": "dea4964a-ff50-4ecf-9201-027981a1566e","timestamp": 1650948340914,"customer_id": 1,"customer_name": "Yamada Taro","statement": [{"item_id": 1,"item_name": "Apple","price": 1000,"count": 3,"total": 3000},{"item_id": 2,"item_name": "Orange","price": 2000,"count": 2,"total": 4000}],"total": 7000},{"order_id": "bcc34150-91fa-4bea-83db-d2dbe6f0f30d","timestamp": 1650948412766,"customer_id": 1,"customer_name": "Yamada Taro","statement": [{"item_id": 5,"item_name": "Melon","price": 3000,"count": 1,"total": 3000}],"total": 3000}]}
...
Check credit total
Get the credit total for customer ID 1 by running the following command:
./gradlew run --args="GetCustomerInfo 1"
You should see the following output, which shows that customer ID 1 has reached their credit_limit in credit_total and cannot place anymore orders:
...
{"id": 1, "name": "Yamada Taro", "credit_limit": 10000, "credit_total": 10000}
...
Try to place an order for one grape and one mango by running the following command:
./gradlew run --args="PlaceOrder 1 3:1,4:1"
You should see the following output, which shows that the order failed because the credit_total amount would exceed the credit_limit amount.
...
java.lang.RuntimeException: Credit limit exceeded
at sample.Sample.placeOrder(Sample.java:205)
at sample.command.PlaceOrderCommand.call(PlaceOrderCommand.java:33)
at sample.command.PlaceOrderCommand.call(PlaceOrderCommand.java:8)
at picocli.CommandLine.executeUserObject(CommandLine.java:1783)
at picocli.CommandLine.access$900(CommandLine.java:145)
at picocli.CommandLine$RunLast.handle(CommandLine.java:2141)
at picocli.CommandLine$RunLast.handle(CommandLine.java:2108)
at picocli.CommandLine$AbstractParseResultHandler.execute(CommandLine.java:1975)
at picocli.CommandLine.execute(CommandLine.java:1904)
at sample.command.SampleCommand.main(SampleCommand.java:35)
...
Make a payment
To continue making orders, customer ID 1 must make a payment to reduce the credit_total amount.
Make a payment by running the following command:
./gradlew run --args="Repayment 1 8000"
Then, check the credit_total amount for customer ID 1 by running the following command:
./gradlew run --args="GetCustomerInfo 1"
You should see the following output, which shows that a payment was applied to customer ID 1, reducing the credit_total amount:
...
{"id": 1, "name": "Yamada Taro", "credit_limit": 10000, "credit_total": 2000}
...
Now that customer ID 1 has made a payment, place an order for one grape and one melon by running the following command:
./gradlew run --args="PlaceOrder 1 3:1,4:1"
You should see a similar output as below, with a different UUID for order_id, which confirms that the order was successful:
...
{"order_id": "8911cab3-1c2b-4322-9386-adb1c024e078"}
...
Stop the database
To stop the database, stop the Docker container by running the following command:
docker compose down
Reference
To see the source code for the e-commerce application used in this tutorial, see Sample.java.