Developer Guide for ScalarDB Cluster with the Java API
ScalarDB Cluster provides a Java API for developing applications. This document explains how to use the Java API.
Add ScalarDB Cluster Java Client SDK to your build
The ScalarDB Cluster Java Client SDK is available in the Maven Central Repository.
To add a dependency on the ScalarDB Cluster Java Client SDK by using Gradle, use the following:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.scalar-labs:scalardb-cluster-java-client-sdk:3.17.1'
}
To add a dependency by using Maven, use the following:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.scalar-labs</groupId>
<artifactId>scalardb-cluster-java-client-sdk</artifactId>
<version>3.17.1</version>
</dependency>
Client modes
The ScalarDB Cluster Java Client SDK supports two client modes: indirect and direct-kubernetes. The following describes the client modes.
indirect client mode
This mode simply sends a request to any cluster node (typically via a load balancer, such as Envoy), and the cluster node receiving the request routes the request to the appropriate cluster node that has the transaction state.
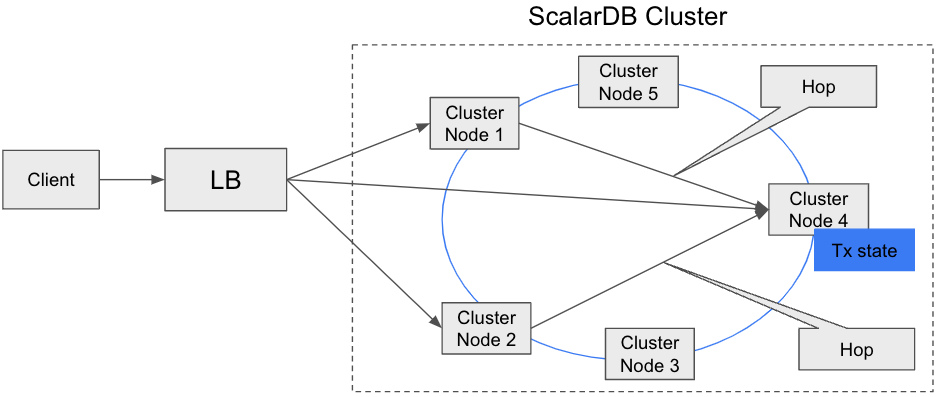
The advantage of this mode is that we can keep the client thin. The disadvantage is that we need an additional hop to reach the correct cluster node, which may affect performance.
You can use this connection mode even if your application is running on a different Kubernetes cluster and your application can't access the Kubernetes API and each cluster node.
If your application is running on the same Kubernetes cluster as your ScalarDB Cluster nodes, you can use the direct-kubernetes client mode.
direct-kubernetes client mode
In this mode, the client uses the membership logic (using the Kubernetes API) and the distribution logic (consistent hashing algorithm) to find the right cluster node that has the transaction state. The client then sends a request to the cluster node directly.
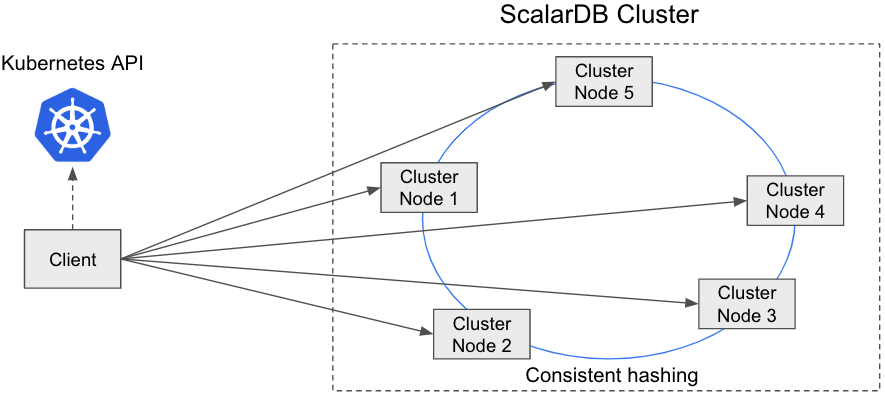
The advantage of this mode is that we can reduce the hop count to reach the proper cluster node, which will improve the performance. The disadvantage of this mode is that we need to make the client fat because the client needs to have membership logic and request-routing logic.
Since this connection mode needs to access the Kubernetes API and each cluster node, you can use this connection mode only if your application is running on the same Kubernetes cluster as your ScalarDB Cluster nodes.
If your application is running on a different Kubernetes cluster, use the indirect client mode.
For details about how to deploy your application on Kubernetes with direct-kubernetes client mode, see Deploy your client application on Kubernetes with direct-kubernetes mode.
ScalarDB Cluster Java API
The ScalarDB Cluster Java Client SDK provides a Java API for applications to access ScalarDB Cluster. The following diagram shows the architecture of the ScalarDB Cluster Java API.
+------------------+
| User/Application |
+------------------+
↓ Java API
+--------------+
| ScalarDB API |
+--------------+
↓ gRPC
+------------------+
| ScalarDB Cluster |
+------------------+
↓ DB vendor–specific protocol
+----+
| DB |
+----+
Using the ScalarDB Cluster Java API is almost the same as using the ScalarDB Java API except the client configurations and Schema Loader are different. For details, see ScalarDB Java API Guide.
The following section describes the Schema Loader for ScalarDB Cluster.
Schema Loader for Cluster
To load a schema via ScalarDB Cluster, you need to use the dedicated Schema Loader for ScalarDB Cluster (Schema Loader for Cluster). Using the Schema Loader for Cluster is basically the same as using the ScalarDB Schema Loader except the name of the JAR file is different. You can download the Schema Loader for Cluster from ScalarDB Releases. After downloading the JAR file, you can run Schema Loader for Cluster with the following command:
java -jar scalardb-cluster-schema-loader-3.17.1-all.jar --config <PATH_TO_SCALARDB_PROPERTIES_FILE> --schema-file <PATH_TO_SCHEMA_FILE> --coordinator
You can also pull the Docker image from the Scalar container registry by running the following command, replacing the contents in the angle brackets as described:
docker run --rm -v <PATH_TO_YOUR_LOCAL_SCALARDB_PROPERTIES_FILE>:/scalardb.properties -v <PATH_TO_YOUR_LOCAL_SCHEMA_FILE>:/schema.json ghcr.io/scalar-labs/scalardb-cluster-schema-loader:3.17.1 --config /scalardb.properties --schema-file /schema.json --coordinator
ScalarDB Cluster SQL
ScalarDB Cluster SQL can be accessed via JDBC and Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB in Java as follows:
+-----------------------------------------+
| User/Application |
+-----------------------------------------+
↓ ↓ Java API
Java API ↓ +-------------------------------+
(JDBC) ↓ | Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB |
↓ +-------------------------------+
+----------------------------------------------+
| ScalarDB JDBC (ScalarDB SQL) |
+----------------------------------------------+
↓ gRPC
+----------------------+
| ScalarDB Cluster SQL |
+----------------------+
↓ DB vendor–specific protocol
+----+
| DB |
+----+
This section describes how to use ScalarDB Cluster SQL though JDBC and Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB.
ScalarDB Cluster SQL via JDBC
Using ScalarDB Cluster SQL via JDBC is almost the same using ScalarDB JDBC except for how to add the JDBC driver to your project.
In addition to adding the ScalarDB Cluster Java Client SDK as described in Add ScalarDB Cluster Java Client SDK to your build, you need to add the following dependencies to your project:
To add the dependencies on the ScalarDB Cluster JDBC driver by using Gradle, use the following:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.scalar-labs:scalardb-sql-jdbc:3.17.1'
implementation 'com.scalar-labs:scalardb-cluster-java-client-sdk:3.17.1'
}
To add the dependencies by using Maven, use the following:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.scalar-labs</groupId>
<artifactId>scalardb-sql-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>3.17.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.scalar-labs</groupId>
<artifactId>scalardb-cluster-java-client-sdk</artifactId>
<version>3.17.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Other than that, using ScalarDB Cluster SQL via JDBC is the same as using ScalarDB JDBC. For details about ScalarDB JDBC, see ScalarDB JDBC Guide.
ScalarDB Cluster SQL via Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB
Similar to ScalarDB Cluster SQL via JDBC, using ScalarDB Cluster SQL via Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB is almost the same as using Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB except for how to add it to your project.
In addition to adding the ScalarDB Cluster Java Client SDK as described in Add ScalarDB Cluster Java Client SDK to your build, you need to add the following dependencies to your project:
To add the dependencies by using Gradle, use the following:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.scalar-labs:scalardb-sql-spring-data:3.17.1'
implementation 'com.scalar-labs:scalardb-cluster-java-client-sdk:3.17.1'
}
To add the dependencies by using Maven, use the following:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.scalar-labs</groupId>
<artifactId>scalardb-sql-spring-data</artifactId>
<version>3.17.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.scalar-labs</groupId>
<artifactId>scalardb-cluster-java-client-sdk</artifactId>
<version>3.17.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Other than that, using ScalarDB Cluster SQL via Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB is the same as using Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB. For details about Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB, see Guide of Spring Data JDBC for ScalarDB.
SQL CLI
Like other SQL databases, ScalarDB SQL also provides a CLI tool where you can issue SQL statements interactively in a command-line shell.
You can download the SQL CLI for Cluster from ScalarDB Releases. After downloading the JAR file, you can run the SQL CLI with the following command:
java -jar scalardb-cluster-sql-cli-3.17.1-all.jar --config <PATH_TO_SCALARDB_SQL_PROPERTIES_FILE>
You can also pull the Docker image from the Scalar container registry by running the following command, replacing the contents in the angle brackets as described:
docker run --rm -it -v <PATH_TO_YOUR_LOCAL_SCALARDB_SQL_PROPERTIES_FILE>:/scalardb-sql.properties ghcr.io/scalar-labs/scalardb-cluster-sql-cli:3.17.1 --config /scalardb-sql.properties
Usage
You can see the CLI usage with the -h option as follows:
java -jar scalardb-cluster-sql-cli-3.17.1-all.jar -h
Usage: scalardb-sql-cli [-hs] -c=PROPERTIES_FILE [-e=COMMAND] [-f=FILE]
[-l=LOG_FILE] [-o=<outputFormat>] [-p=PASSWORD]
[-u=USERNAME]
Starts ScalarDB SQL CLI.
-c, --config=PROPERTIES_FILE
A configuration file in properties format.
-e, --execute=COMMAND A command to execute.
-f, --file=FILE A script file to execute.
-h, --help Display this help message.
-l, --log=LOG_FILE A file to write output.
-o, --output-format=<outputFormat>
Format mode for result display. You can specify
table/vertical/csv/tsv/xmlattrs/xmlelements/json/a
nsiconsole.
-p, --password=PASSWORD A password to connect.
-s, --silent Reduce the amount of informational messages
displayed.
-u, --username=USERNAME A username to connect.
Further reading
If you want to use ScalarDB Cluster in programming languages other than Java, you can use the ScalarDB Cluster gRPC API. For details about the ScalarDB Cluster gRPC API, refer to the following:
JavaDocs are also available: